


Next: 10.1 Types of operations
Up: Some Lectures on Number
Previous: 9.5 Frobenius Endomorphism
First we formulate a general (deterministic) cryptosystem. Let M
denote the set of all possible message chunks, let C denote the
corresponding set of all cipher-text chunks. Let P be the set of all
possible public keys and S the set of all possible secret keys. A
general cryptosystem can be thought of as a pair of maps: the
encryption map
E : M×P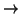 C and the decryption map
D : C×S
C and the decryption map
D : C×S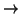 M. In addition we need an assignment map a : P
M. In addition we need an assignment map a : P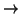 S. The
condition these maps must satisfy is that for each p
S. The
condition these maps must satisfy is that for each p 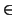 P the map
Da(p)oEp : M
P the map
Da(p)oEp : M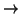 M must be identity. In a symmetric-key system
the map a is the identity; in other words there is a single key
space K = P = S for encryption as well as decryption. In modern use
such systems are used in contexts where the operations must be very
rapid. Thus it is also customary to assume that M and C are of
roughly the same size; for simplicity let us say V = M = C. Thus a
symmetric-key system can be modelled as
E : V×K
M must be identity. In a symmetric-key system
the map a is the identity; in other words there is a single key
space K = P = S for encryption as well as decryption. In modern use
such systems are used in contexts where the operations must be very
rapid. Thus it is also customary to assume that M and C are of
roughly the same size; for simplicity let us say V = M = C. Thus a
symmetric-key system can be modelled as
E : V×K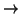 V and
D : V×K
V and
D : V×K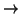 V. It follows then that for each key k we obtain a
permutation of the set V. Thus one naive approach would be to take
K to be the collection of all permutations of V. However, we need
to ensure that K is somewhat smaller than M as it would be rather
pointless to exchange large length keys in order to exchange short
messages! Secondly it is also clear that permutations that are of
small order are risky as these patterns could be spotted. More
generally, it is also a bad idea for K to be a subgroup of the
permutation group as group theoretic relations between different keys
could be used to attack the cryptosystem. A symmetric key
cryptosystem thus attempts to obtain a ``good'' selection K of
permutations of the set V.
V. It follows then that for each key k we obtain a
permutation of the set V. Thus one naive approach would be to take
K to be the collection of all permutations of V. However, we need
to ensure that K is somewhat smaller than M as it would be rather
pointless to exchange large length keys in order to exchange short
messages! Secondly it is also clear that permutations that are of
small order are risky as these patterns could be spotted. More
generally, it is also a bad idea for K to be a subgroup of the
permutation group as group theoretic relations between different keys
could be used to attack the cryptosystem. A symmetric key
cryptosystem thus attempts to obtain a ``good'' selection K of
permutations of the set V.
To summarise, a symmetric-key cryptosystem consists of a map
K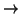 Perm(V) from a set K of size less than the size of V to the
permutation group of V.
Perm(V) from a set K of size less than the size of V to the
permutation group of V.
Subsections



Next: 10.1 Types of operations
Up: Some Lectures on Number
Previous: 9.5 Frobenius Endomorphism
Kapil Hari Paranjape
2002-10-20
![]() Perm(V) from a set K of size less than the size of V to the
permutation group of V.
Perm(V) from a set K of size less than the size of V to the
permutation group of V.